Auschwitz Extermination Camp
Auschwitz Birkenau – updated 10 January 2023.
The Auschwitz Birkenau complex has left its inglorious mark on human history. A symbol of the Holocaust, during its five years of operation over a million Jews, along with Poles, Romani and other groups, were systematically killed by German Occupiers in WWII. Confronting and emotionally charged, a visit to the complex is an essential part of the human experience.

Atrocities
Both sections of the camp, Auschwitz I and the much larger outlying Birkenau (Auschwitz II) have been preserved and are open to visitors. Everyone should visit Auschwitz at least once in their lives, it is a stern reminder of the horrors that human beings can inflict on each other and the only way to understand the extent and horror of the place and the atrocities that took place there.

Oświęcim
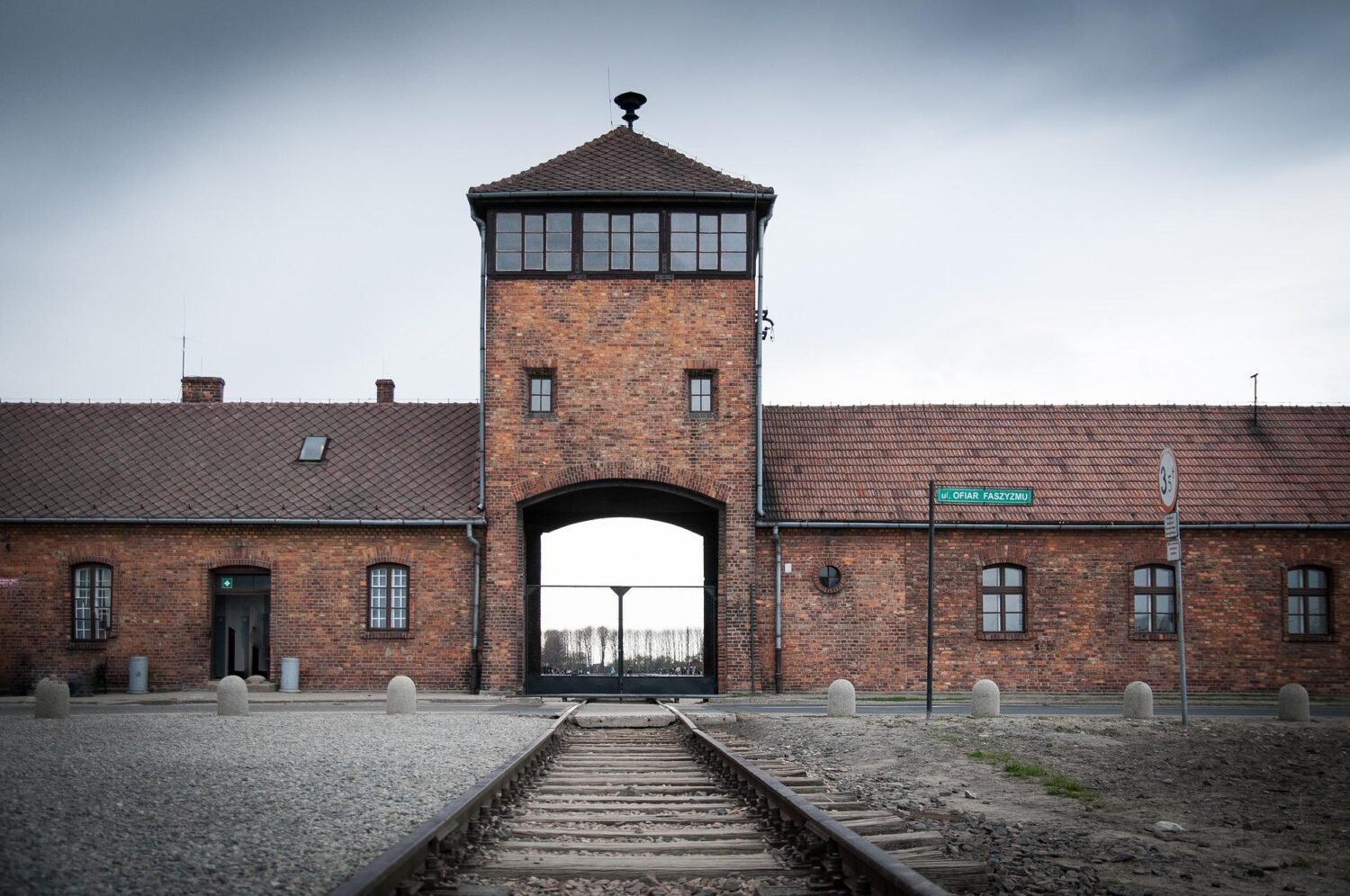
The Auschwitz extermination camp was established in Polish army barracks on the outskirts of Oświęcim by the Germans in April 1940 and was originally intended for Polish political prisoners. It was then adapted for the wholesale extermination of the Jews of Europe in fulfilment of German Nazi ideology and pursuit of the ‘final solution of the Jewish question in Europe.’
For this purpose, the much larger camp at Birkenau was built 2km west of the original site in 1941/1942, followed by another one in Monowitz, several kilometres to the west.

Birkenau
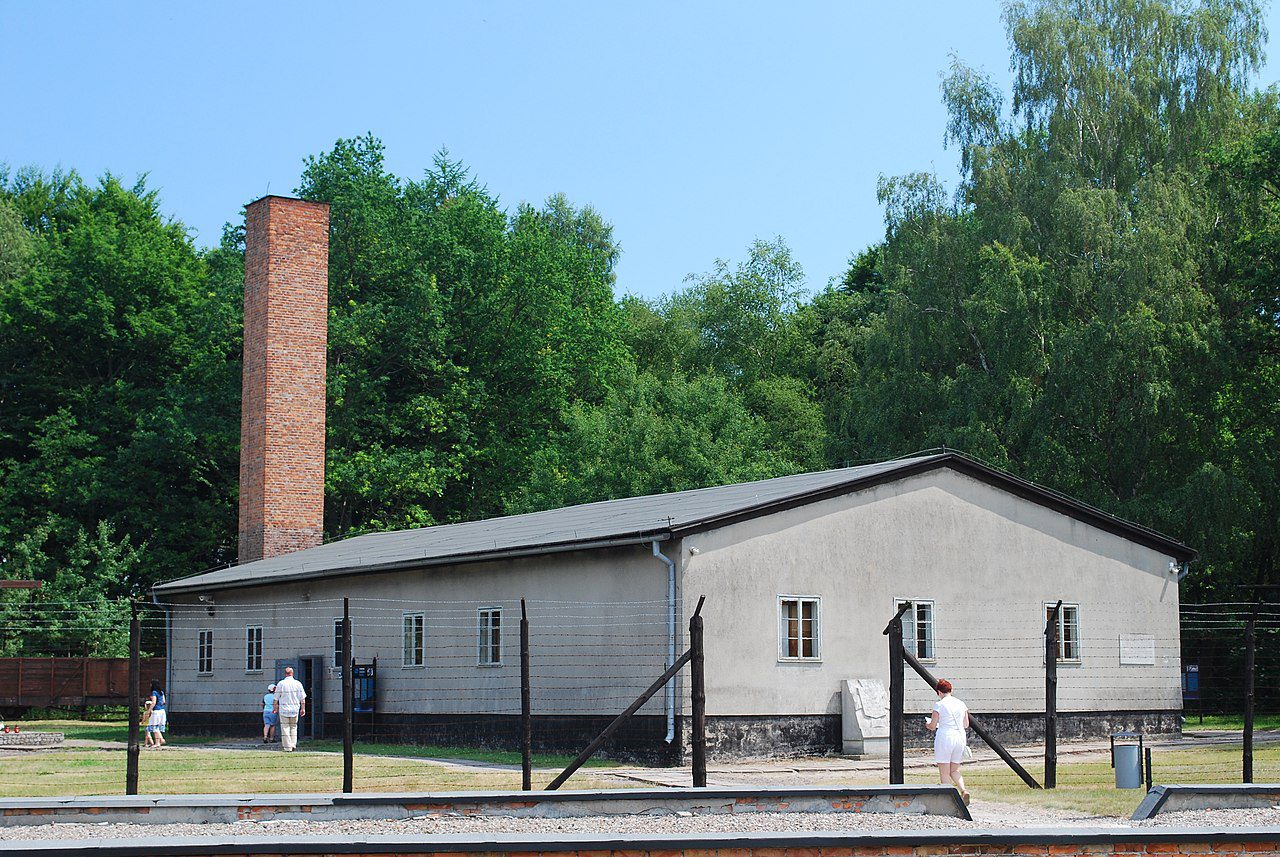
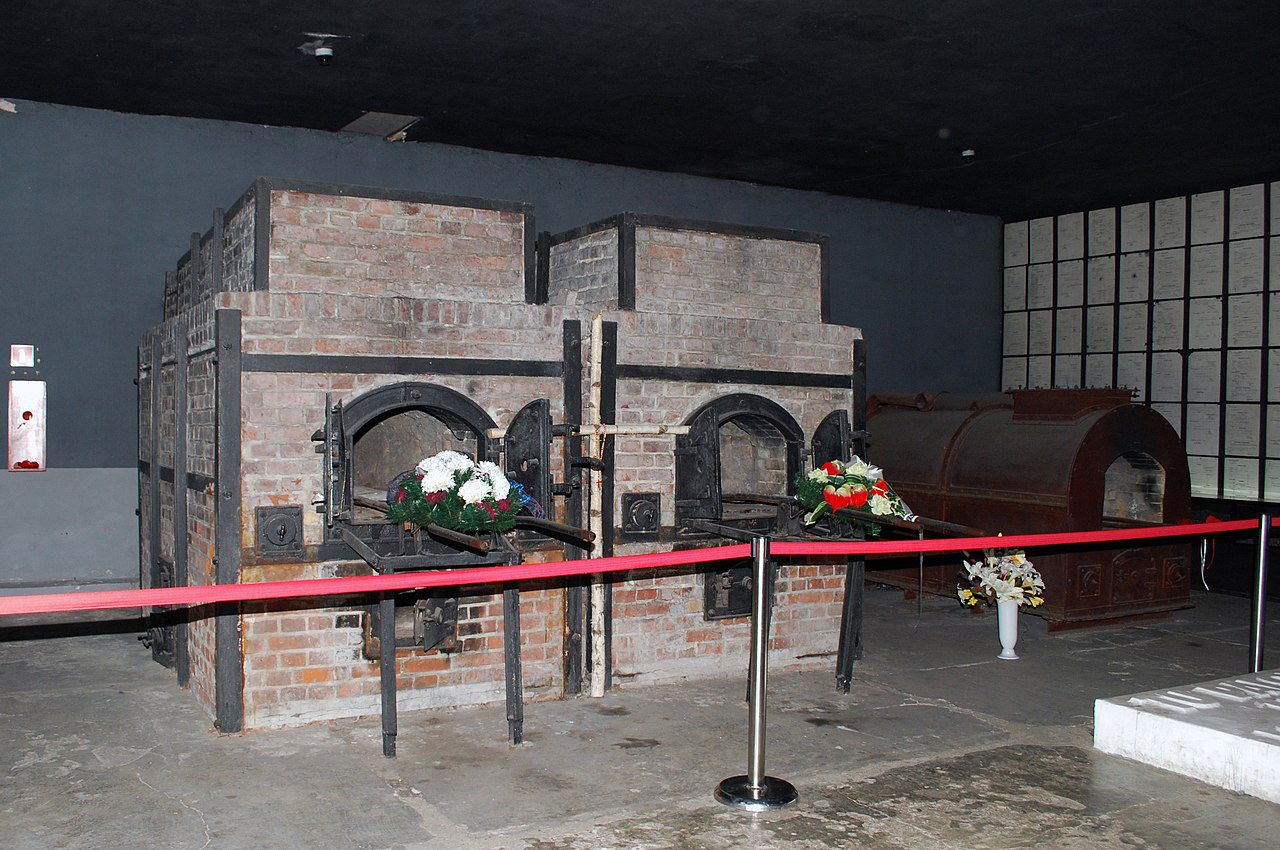
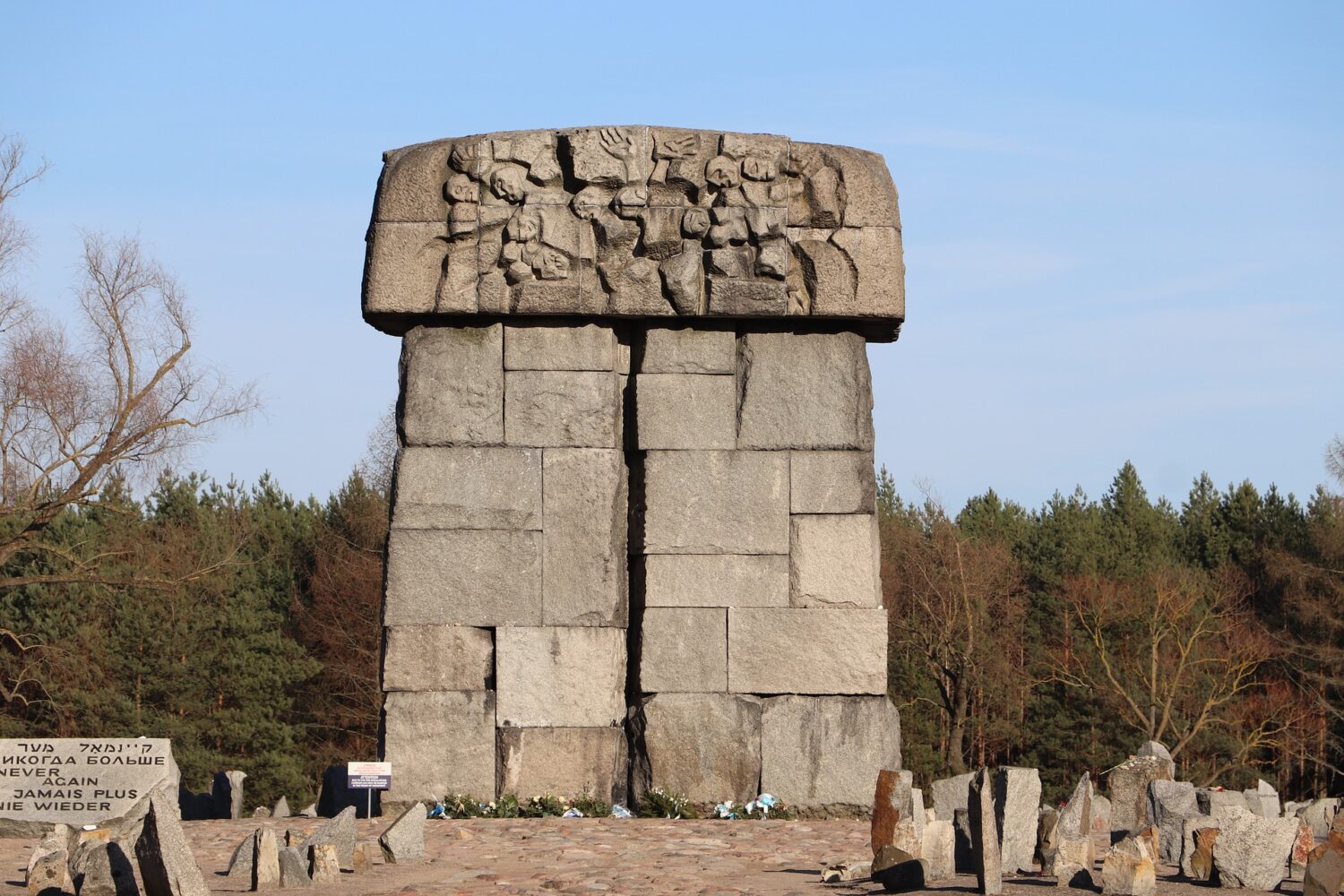
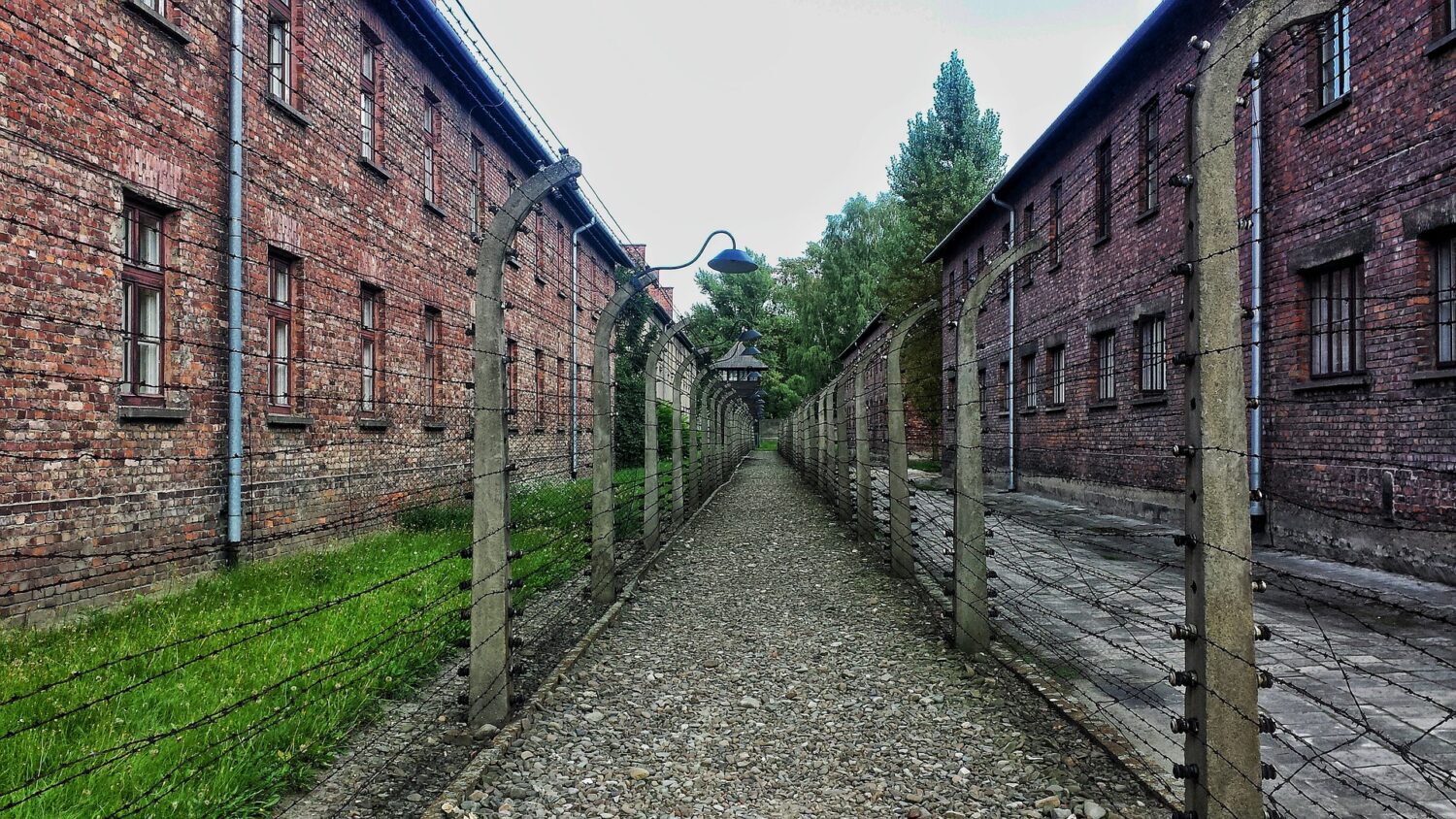
Most of the killing took place in Birkenau and not Auschwitz. The 175 hectares camp was purpose-built for efficiency with 300 prison barracks housing 300 people each and four huge gas chambers, complete with crematoria. Each gas chamber could asphyxiate 2,000 people at one time and were fitted with electric lifts to raise the bodies to the ovens more quickly and conveniently.
Rudolf Höss
From spring 1942 until the fall of 1944, transport trains delivered Jews to the camp’s gas chambers from all over Nazi-occupied Europe. The camp’s first commandant, Rudolf Höss, testified after the war at the Nuremberg Trials that up to three million people had died there (2.5 million exterminated, and 500,000 from disease and starvation), a figure since revised to 1.1 million. Of the 1.1 million people who were murdered in Birkenau, 90 percent of them were Jews.

Medical experiments
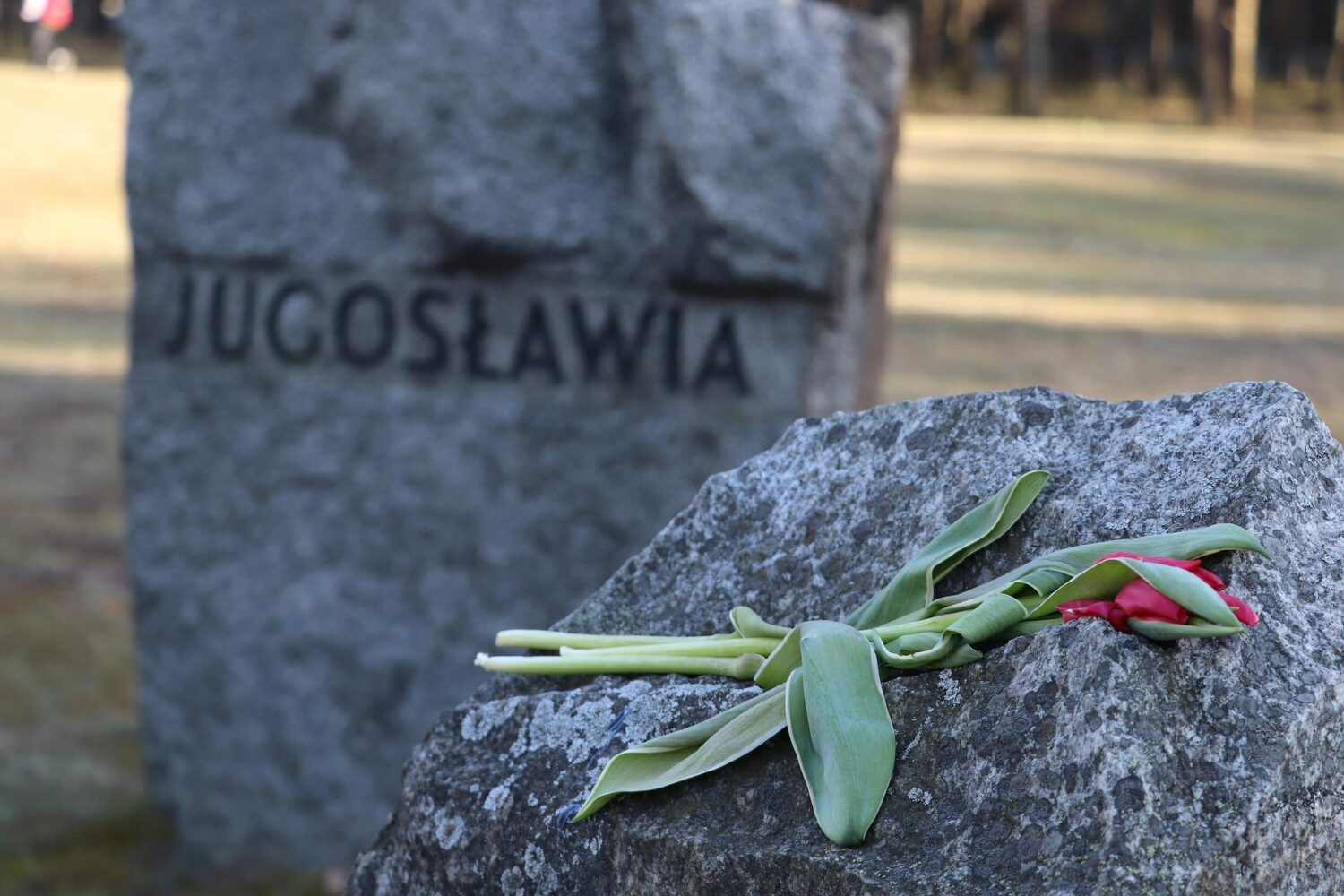
Others deported to Auschwitz Birkenau included 150,000 Poles, 23,000 Roma and Sinti, 15,000 Soviet prisoners of war, and tens of thousands of people of diverse nationalities. Those not killed in the gas chambers died of starvation, forced labour, lack of disease control, individual executions, and medical experiments.
Selections
By July 1942, the SS were conducting the infamous “selections,” in which incoming Jews were divided into those deemed able to work, who were sent to the right and admitted into the camp, and those who were sent to the left and immediately gassed.

Daily convoys
Prisoners were transported from all over German-occupied Europe by rail, arriving in daily convoys. The group selected to die, about three-quarters of the total, included almost all children, women with children, all the elderly, and all those who appeared on brief and superficial inspection by an SS doctor not to be completely fit. Auschwitz II-Birkenau claimed more victims than any other German extermination camp, despite coming into use after all the others.
Gas chamber
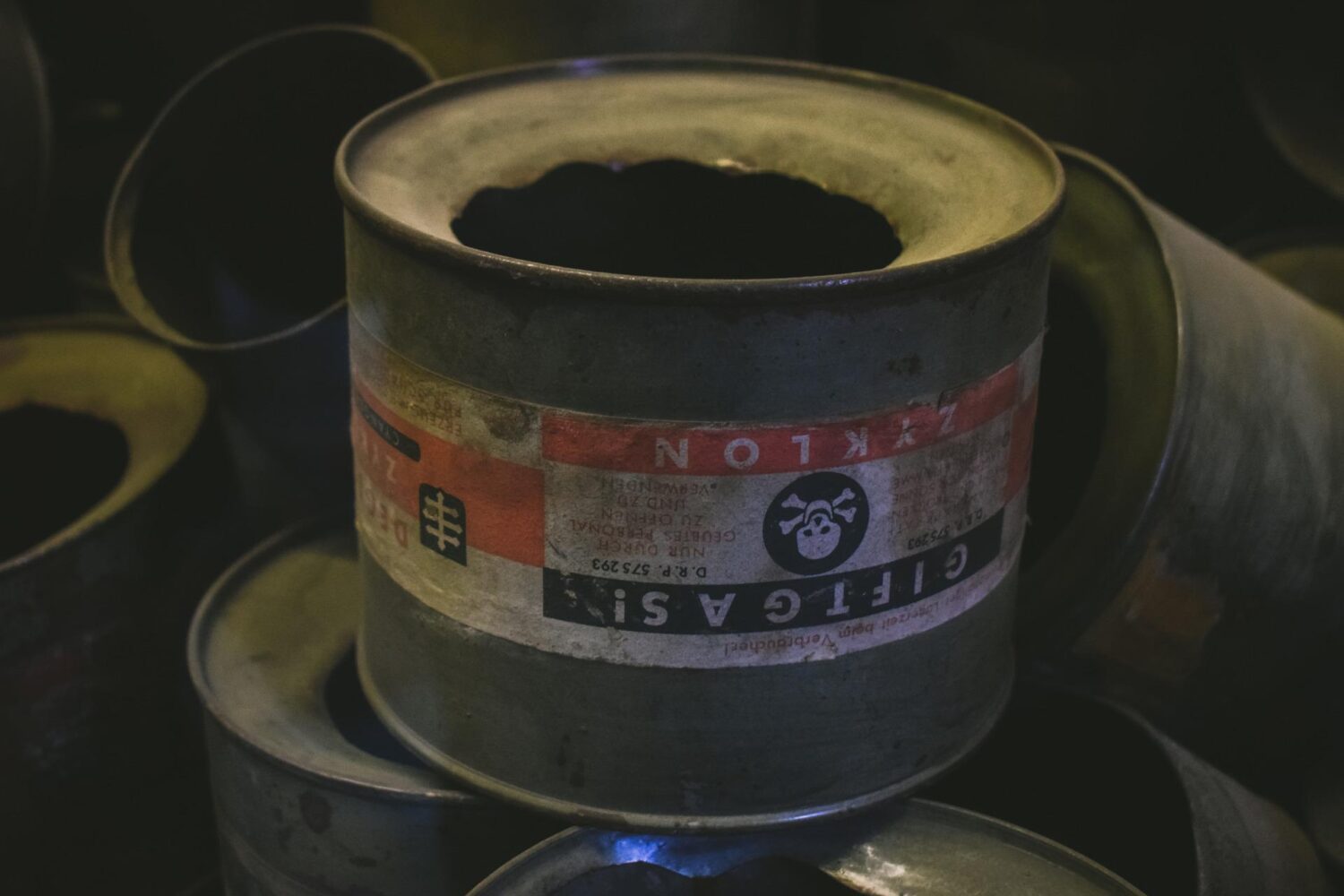
SS officers told the victims they were to take a shower and undergo delousing. The victims would undress in an outer chamber and walk into the gas chamber, which was disguised as a shower facility, complete with dummy shower heads. After the doors were shut, SS men would dump in the cyanide pellets via holes in the roof or windows on the side. In Auschwitz II-Birkenau, more than 20,000 people could be gassed and cremated each day.

Canada
Sonderkommandos removed gold teeth from the corpses of gas chamber victims; the gold was melted down and collected by the SS. The belongings of the arrivals were seized by the SS and sorted in an area of the camp called “Canada,” so-called because Canada was seen as a land of plenty. Many of the SS at the camp enriched themselves by pilfering the confiscated property.
Heinrich Himmler
The last selection took place on October 30, 1944. The next month, Heinrich Himmler ordered the crematoria destroyed before the Red Army reached the camp. The gas chambers of Birkenau were blown up by the SS in January 1945 in an attempt to hide the German crimes from the advancing Soviet troops. The SS command sent orders on January 17, 1945, calling for the execution of all prisoners remaining in the camp, but in the chaos of the Nazi retreat the order was never carried out. On January 17, 1945, Nazi personnel started to evacuate the facility.
Death March
Nearly 60,000 prisoners were forced on a death march toward a camp in Wodzisław Śląski (German: Loslau). Those too weak or sick to walk were left behind. These remaining 7,500 prisoners were liberated by the 322nd Rifle Division of the Red Army on January 27, 1945.
Bergen-Belsen
Approximately 20,000 Auschwitz Birkenau prisoners made it to Bergen-Belsen concentration camp in Germany, where they were liberated by the British in April 1945. Among the artefacts of automated murder found by the Russians were 348,820 men’s suits and 836,255 women’s garments.
On January 27, 1945, Auschwitz Birkenau was liberated by Soviet troops, a day commemorated around the world as International Holocaust Remembrance Day.
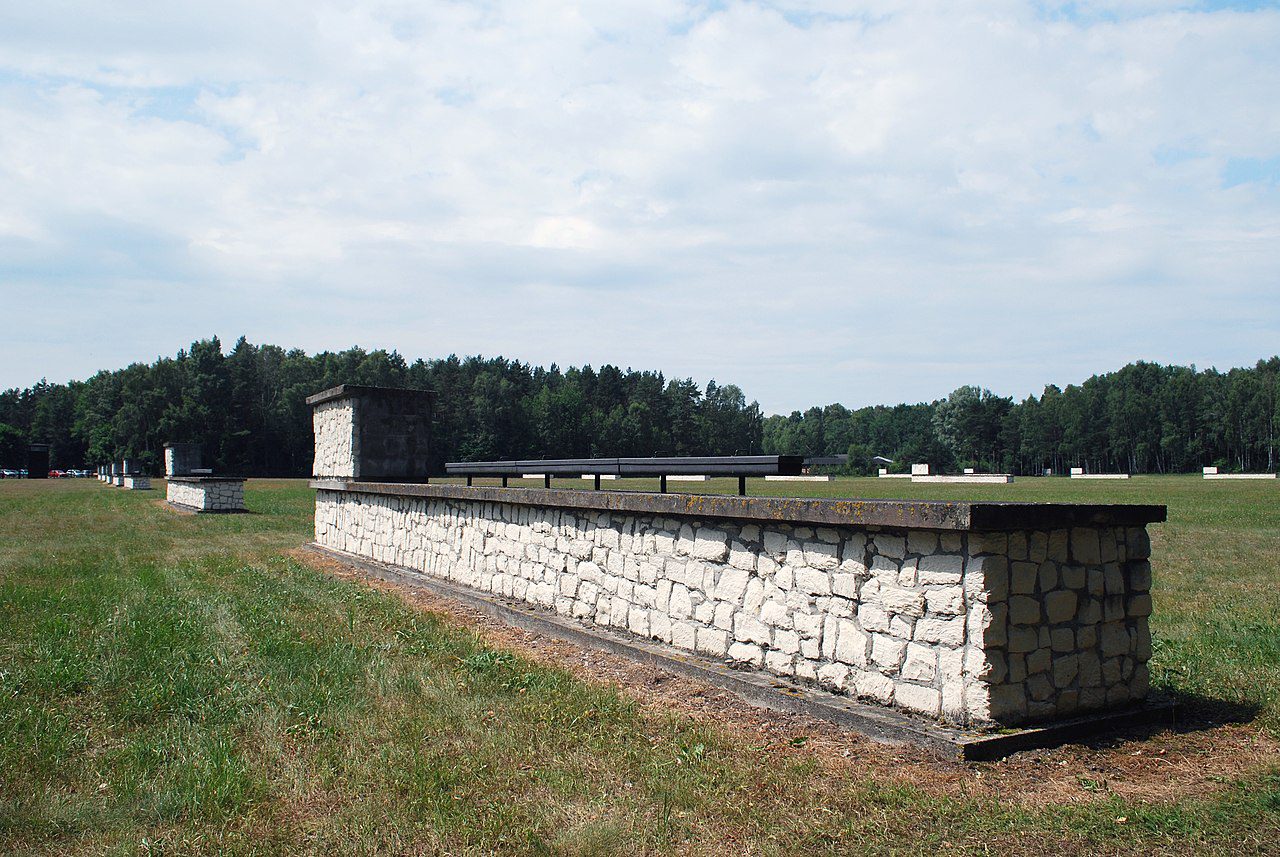
Today, at Birkenau the entrance building and some of the southern brick-built barracks survive; but of the almost 300 wooden barracks, only 19 remain: 18 near the entrance building and one, on its own, farther away. All that survives of the others are chimneys, remnants of a largely ineffective means of heating. Many of these wooden buildings were constructed from prefabricated sections made by a company that intended them to be used as stables; inside, numerous metal rings for the tethering of horses can still be seen.
Museum
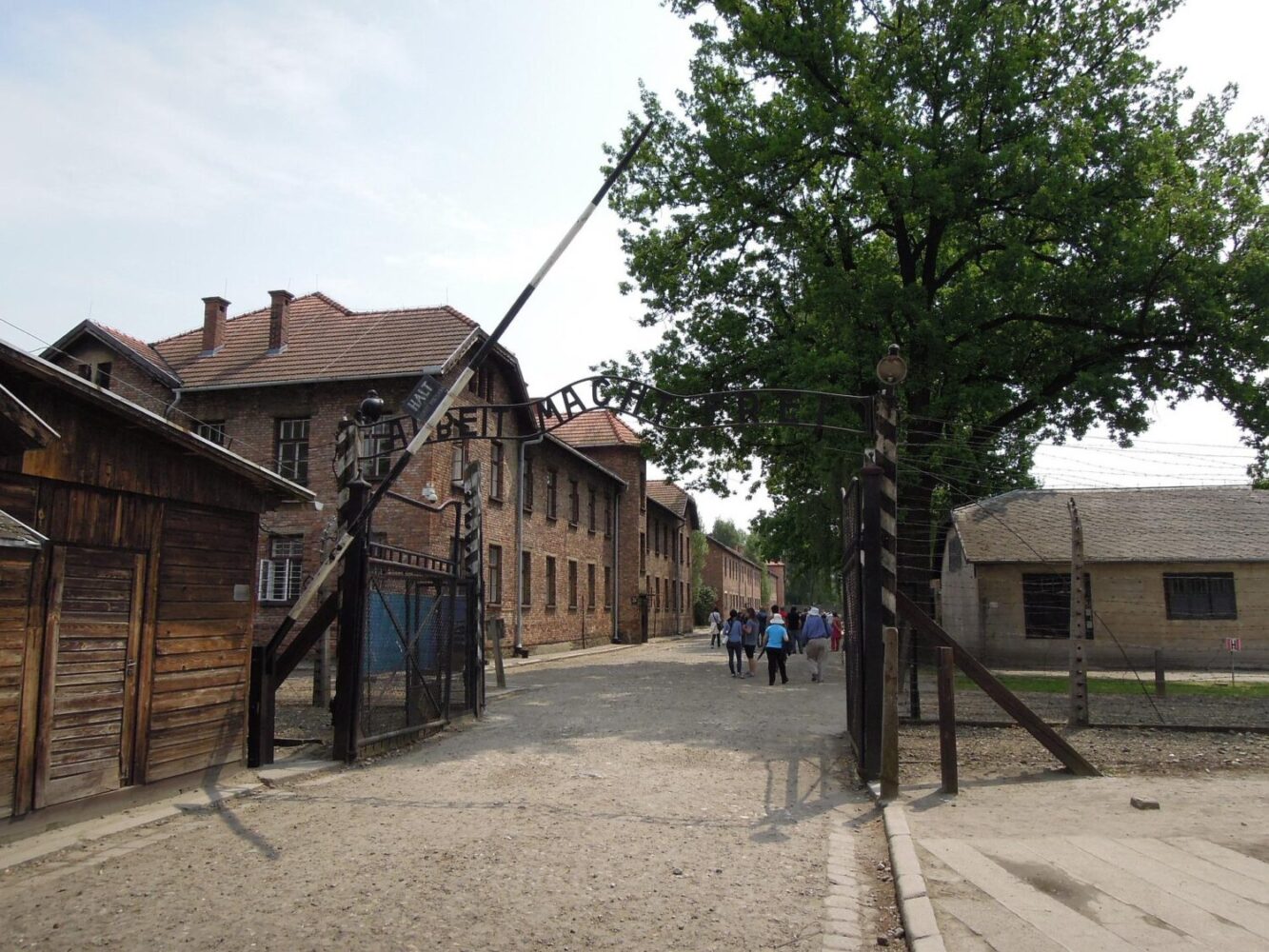
The Polish government decided to restore Auschwitz I and turn it into a museum honouring the victims of Nazism; Auschwitz II, where buildings (many of which were prefabricated wood structures) were prone to decay, was preserved but not restored. Today, the Auschwitz I museum site combines elements from several periods into a single complex: for example, the gas chamber at Auschwitz I (which had been converted into an air-raid shelter for the SS) was restored and the fence was moved (because of building work being done after the war but before the museum was established). However, in most cases the departure from the historical truth is minor and is clearly labelled.
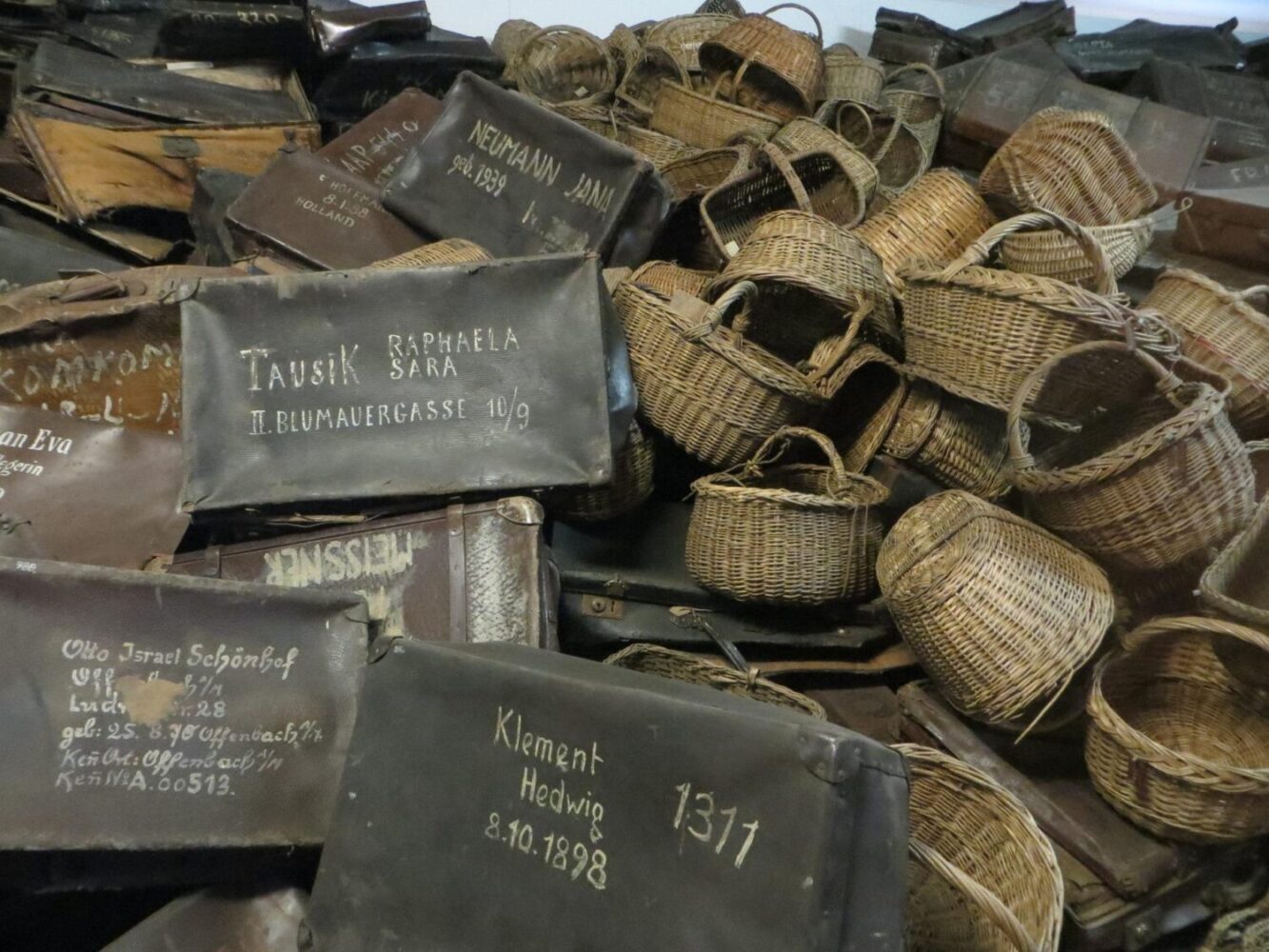
The museum contains many men’s, women’s and children’s shoes taken from their victims; also, suitcases, which the deportees were encouraged to bring with them, and many household utensils. One display case, some 30 metres (98 ft) long, is wholly filled with human hair which the Nazis gathered from people before they were sent to labour or before and after they were killed.
Auschwitz II and the remains of the gas chambers there are open to the public. The camp is on the list of UNESCO World Heritage Sites. The ashes of the victims were scattered between the huts, and the entire area is regarded as a grave site. Most of the buildings of Auschwitz I are still standing. The public entrance area is outside the perimeter fence in what was the camp admission building, where new prisoners were registered and given their uniforms. At the far end of Birkenau are memorial plaques in many languages, including Romani.
FAQ
Auschwitz-Birkenau is a former Nazi concentration and extermination camp located in Poland. It is a site of great historical significance and is visited by millions of people each year. Here are some frequently asked questions about visiting Auschwitz-Birkenau:
Where is Auschwitz-Birkenau located?
Auschwitz-Birkenau is located in the city of Oswiecim, which is in southern Poland, near the border with the Czech Republic. The camp is located about 70 miles west of Krakow.
Is it possible to visit Auschwitz-Birkenau?
Yes, it is possible to visit the camp, but visitors are required to take a guided tour. Guided tours are available in multiple languages and last around 3 hours.
How much does it cost to visit Auschwitz-Birkenau?
Entrance to the camp is free, but tours are offered for a fee, as of 2021 it was 25 PLN (Polish zloty) for adult.
Are there any restrictions on visiting the camp?
Some areas of the camp may be inaccessible to visitors with mobility issues. Photography is not allowed inside the camp, but you can take some images of the exterior.
Is there a dress code for visiting Auschwitz-Birkenau?
It’s not officially a dress code, but it is respectful to wear an appropriate clothing when visiting, since it is a place of historic importance and a cemetery where many innocent people lost their lives.
What should I expect when I visit the camp?
Visiting Auschwitz-Birkenau can be a deeply moving and emotional experience. Visitors will have the opportunity to see the former living quarters of prisoners, the gas chambers, and the crematoria. Visitors are also taken on a guided tour of the camp, during which the guide provides historical information about the camp and the events that occurred there.
Where can I find more information?
The official website of the Auschwitz-Birkenau Memorial and Museum provides a wealth of information about visiting the camp, including tour schedules, visitor information, and educational resources.
Read about the Dentist of Auschwitz.